Crude Relations: Many U.S. Voters Back Closer Ties With Dictators for Cheaper Oil
As gas prices in the United States reach historic highs, President Joe Biden heads to Saudi Arabia next month to improve ties with the state he once promised to make a “pariah,” but voters aren’t necessarily warming to the idea of reaching out to dictators for in a bid for cheaper gas, a new Morning Consult/Politico survey shows, with support for such efforts down slightly since March.
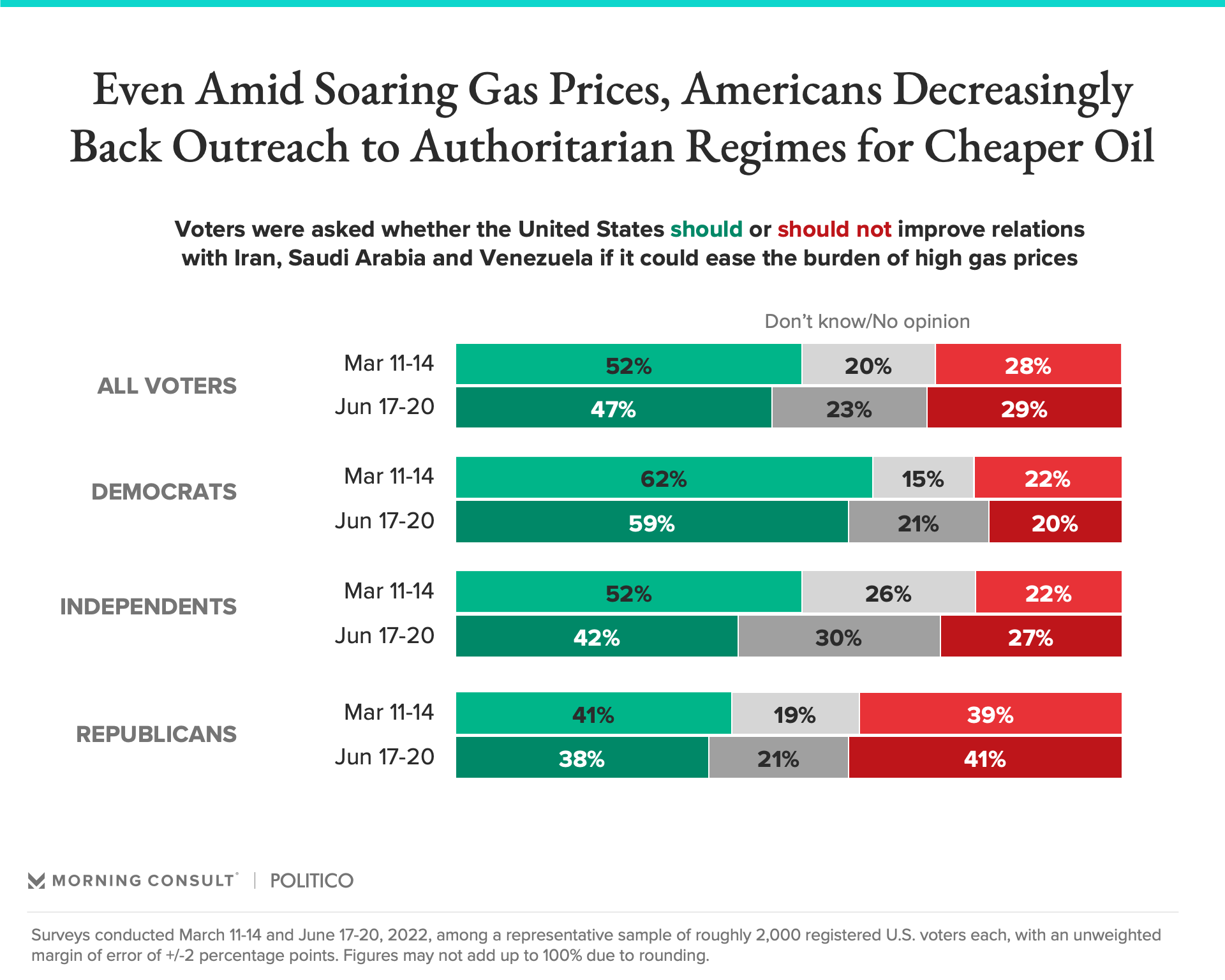
Soaring gas prices aren’t making outreach to dictators more appealing
- The share of voters who back U.S. efforts to improve ties with Iran, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela if it could make gas cheaper has fallen from 52% to 47% since mid-March, with the decline most pronounced among independents (from 52% to 42%).
- Democrats are still the most likely to support entreaties to leaders like Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in search of cheaper oil, with nearly three times as many backing the idea (59%) as those who oppose it (20%).
- Republicans narrowly oppose reaching out to Iran, Venezuela and Saudi Arabia, with 41% opposed to 38% in support — figures almost unchanged since March.
Biden’s rapprochement with Riyadh might not pay off
The White House has confirmed Biden will meet with Crown Prince Mohammed during his trip to the Middle East next month, despite the president’s previous blistering criticism of the kingdom’s de facto ruler, whom a U.S. intelligence report said approved the murder of Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi at the Saudi consulate in Turkey in 2018.
Though administration officials have been quick to clarify the visit is part of a broader meeting of the Riyadh-based Gulf Cooperation Council, news of Biden’s plans to visit the kingdom first surfaced earlier this month after the OPEC+ oil cartel, which is essentially led by Saudi Arabia, agreed to pump more oil and counteract the deficits in global markets left by Western sanctions on Russian fossil fuels.
There’s just one problem for Biden: Oil producers are already pumping about as much as they can. Triple-figure crude prices tend to be more persuasive than diplomacy when it comes to switching on oil spigots at the best of times, and OPEC+ is struggling to ramp up production to meet past output targets.
Meanwhile, it’s hard to see where else Biden can turn for oil, as the breakdown of talks to resume the 2015 Iran nuclear deal and refusal to invite Venezuela to the Summit of the Americas in Los Angeles earlier this month have kept ties with Tehran and Caracas on ice.
At the end of the day, Biden may be satisfied to be seen to be pursuing every possible avenue to alleviate the pain Americans are experiencing at the pump, but even then the lion’s share of voters across the political spectrum look askance at the Saudis.
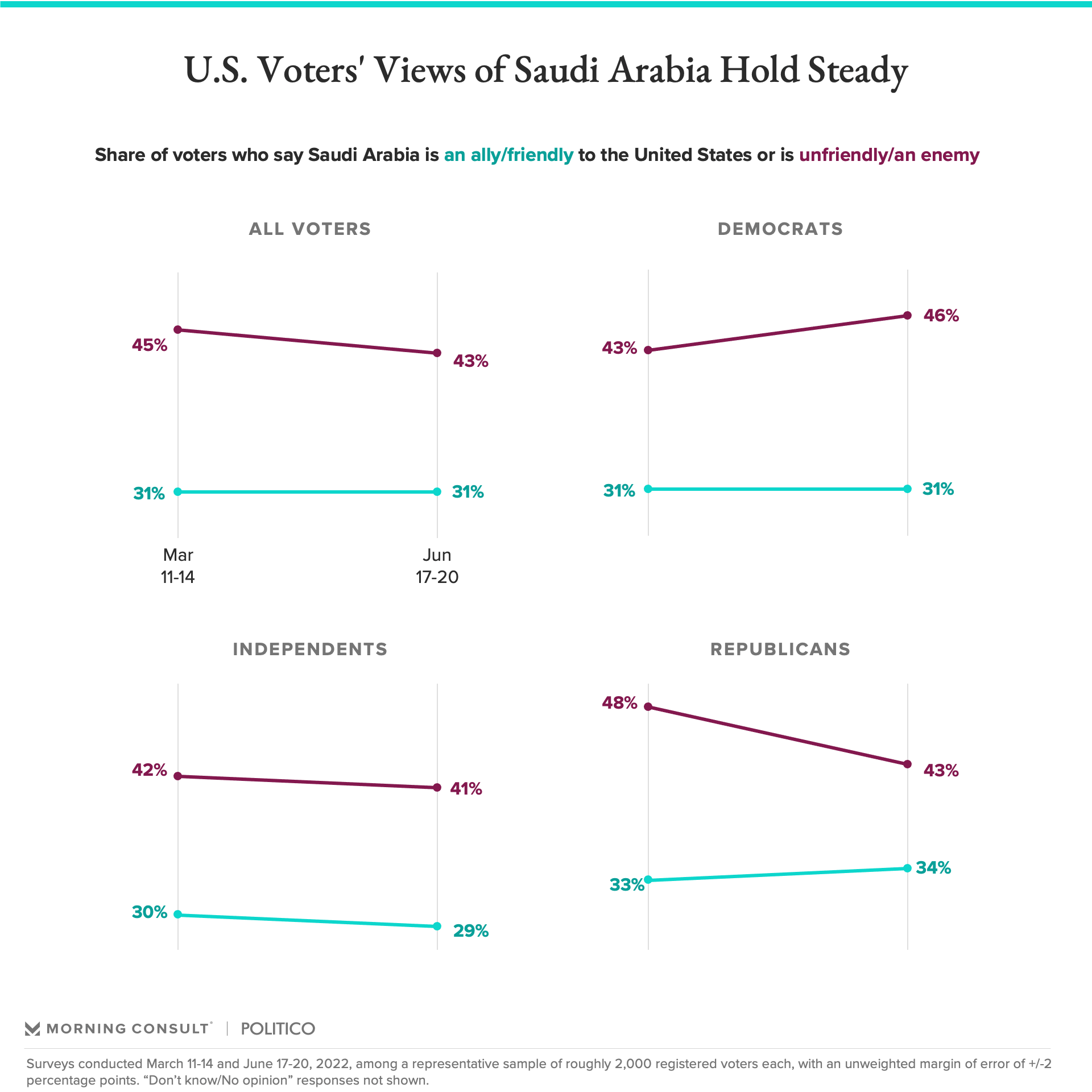
High gas prices don’t make Saudi Arabia seem friendlier
- Voters are more likely to see Saudi Arabia as “unfriendly” or an “enemy” than as “friendly” or “an ally”, and the rise in gas prices has done little to change views.
- Views across the partisan divide are roughly uniform, hinting at the role partisanship plays in increasing support for oil diplomacy among Democrats while depressing it among Republicans.
The latest Morning Consult/Politico survey was conducted June 17-20, 2022, among a representative sample of 2,004 registered U.S. voters, with an unweighted margin of error of plus or minus 2 percentage points.
Matthew Kendrick previously worked at Morning Consult as a data reporter covering geopolitics and foreign affairs.